Automating the Future: Robots and 3D Printers
Robots and 3D Printers: How Robots Enhance 3D Printing Processes

The integration of Robots and 3D printers has transformed manufacturing by combining automation and additive manufacturing. This collaboration offers enhanced precision, efficiency, and customization. Robots assist in various tasks, enabling faster and more accurate production, while 3D printers bring the ability to create complex designs. This symbiotic relationship holds great potential for various industries, paving the way for scalable and innovative manufacturing processes.
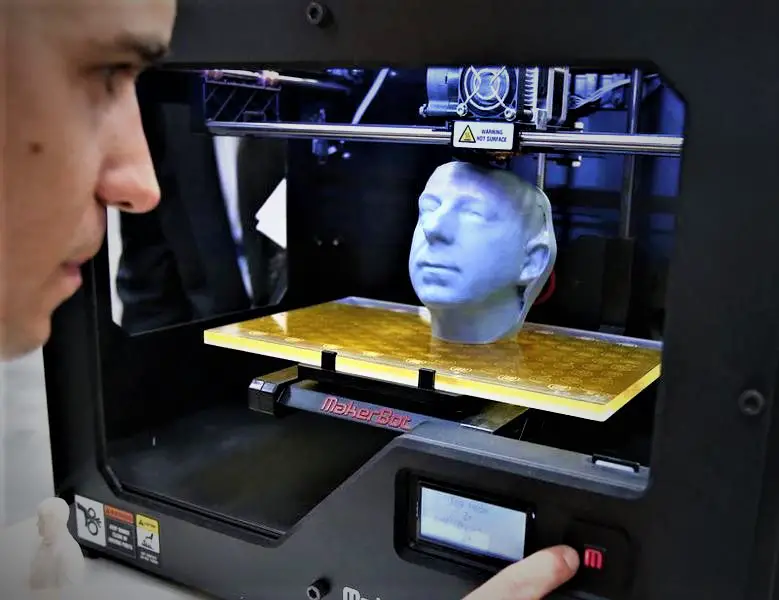

Role of Robots in 3D Printing:
The collaboration between robots and 3D printers introduces automation and precision to the additive manufacturing process. Robots are employed to perform various tasks that optimize the printing workflow, such as material handling, part removal, quality control, and even post-processing tasks like sanding and painting. This integration eliminates the need for human intervention in mundane and repetitive tasks, streamlining the entire production process and enhancing overall efficiency.
Benefits of the Collaboration:
Speed and Efficiency:
Robots can work tirelessly and consistently, leading to faster printing and assembly times. Their ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously ensures a continuous production line, minimizing downtime and increasing overall efficiency.
Precision and Accuracy:
3D printing is known for its high level of accuracy, and by integrating robots, the precision is further enhanced. Robots can manipulate the printer head or build platform with extreme accuracy, resulting in the production of complex and intricate designs that might be challenging for human operators.
Customization:
The combination of robots and 3D printing allows for mass customization. Each product can be personalized according to individual customer requirements without significantly increasing production costs, making it economically feasible to produce unique items on a large scale.
Reduced Waste:
With robots carefully executing 3D printing tasks, there is minimal room for errors, reducing material waste and overall production costs.
Scalability:
By leveraging the collaborative capabilities of robots and 3D printers, manufacturers can easily scale their production output without investing in substantial additional labor.
Real-world Applications:
The integration of 3D printers and robots has found applications across various industries:
Aerospace:
The aerospace industry benefits from the production of lightweight and complex components with high precision using 3D printing and robots.
Automotive:
In the automotive sector, 3D printers and robots have streamlined the production of prototypes, custom parts, and tooling equipment.
Healthcare:
The medical field has witnessed significant advancements in custom prosthetics, implants, and medical devices due to the collaboration between 3D printers and robots.
Construction:
In construction, large-scale 3D printers working in tandem with robots can create prefabricated structures and buildings more efficiently than traditional construction methods.
Electronics:
Robots and 3D printers enable the production of customized electronic components and circuitry with precise dimensions.
Future Possibilities:
As technology continues to advance, the collaboration between 3D printers and robots will undoubtedly evolve. Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable robots to become more autonomous, making decisions during the printing process, and adapting to unexpected situations. Additionally, the development of new materials and improved 3D printing techniques will further expand the possibilities of this partnership, opening up new avenues for innovation and creativity.
Conclusion:
The collaboration between 3D printers and robots marks a transformative phase in the manufacturing landscape. This combination of additive manufacturing and automation offers numerous advantages, including increased efficiency, precision, customization, and reduced waste. As industries continue to adopt this symbiotic approach, we can expect to witness exciting advancements and new applications in various sectors, ultimately reshaping the future of manufacturing and design.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the role of robots in 3D printing?
Robots assist in various tasks in the 3D printing process, including material handling, part removal, quality control, and post-processing activities. Their precision and automation streamline the production workflow.
How do robots enhance 3D printing processes?
Robots bring increased speed, accuracy, and efficiency to 3D printing. They can work tirelessly, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous production. Additionally, their ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously optimizes the overall manufacturing process.
What are the benefits of integrating robots with 3D printers?
The collaboration between robots and 3D printers offers several advantages, including faster production times, improved precision, reduced waste, mass customization, and scalability, making it economically viable for various industries.
Which industries benefit from this symbiosis?
Numerous industries benefit from the integration of robots and 3D printing, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, electronics, construction, and more. It allows for the creation of complex designs and customized products in a cost-effective manner.
Can robots work autonomously in 3D printing?
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning enable robots to work more autonomously during the 3D printing process. They can adapt to unforeseen situations, making decisions to optimize the printing process.
What materials can be used in 3D printing with robots?
3D printing with robots supports various materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biological materials. This versatility allows for the creation of a wide range of products across industries.
How does the collaboration impact the future of manufacturing?
The integration of robots and 3D printers opens up new possibilities for innovation and creativity in manufacturing. It paves the way for smart factories, mass customization, and more sustainable production processes, shaping the future of manufacturing industries.



